The BRCA genes
In 1994 and 1995 the main genes associated with hereditary breast cancer were identified:
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes (BRCA= BReast CAncer genes)
These genes occupy large portions of chromosomes 17 (BRCA1) and 13 (BRCA2), and their normal function is the regulation of cellular division.
About a third of all hereditary breast cancer cases are caused by mutations in the BRCA1 gene, and another third is caused by mutations in the BRCA2. These genetic changes mostly increase the risk of breast cancer, but also contribute for ovarian cancer at a very early age (before the menopause).
A woman who inherits one of these mutations (BRCA1 or BRCA2) has 5 times more chance of developing breast cancer than an average woman (without the mutation), as well as having increased risk of other tumors.
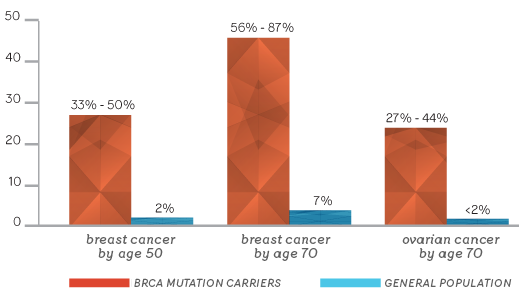
Data is presented as "the estimated risk of developing the disease by age group”.
Learn more about the risks when these genes are mutated: