BRCA2 risk
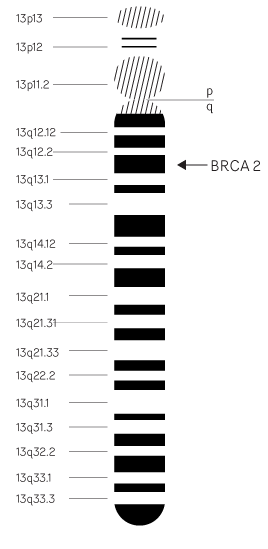 The increase in the risk of disease as result of carrying a BRCA2 mutation is very similar to that of the BRCA1 mutation.
The increase in the risk of disease as result of carrying a BRCA2 mutation is very similar to that of the BRCA1 mutation.
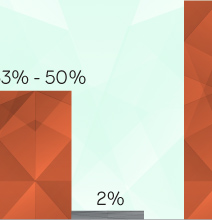
A woman with a BRCA2 mutation has between 52% and 82% chance of developing breast cancer during her life. Her probability of developing ovarian cancer is about 27%.
However, there are differences between the two mutations, especially in men.
The BRCA2 mutation carries a higher risk of breast and/or prostate cancer in men than the BRCA1. A man with a mutated BRCA2 gene has a 6% chance of developing breast cancer in his life.
The BRCA2 is also associated in men with other types of cancer, such as pancreas, stomach, vesicle and bile duct (gallbladder) cancers, as well as skin melanoma.
It is important to remember though:
- Not all the women in a family with hereditary breast cancer will have the mutation;
- Not all the diagnosed cancers will be the result of the hereditary mutation in these families;
- To carry the mutation is not synonymous of cancer, neither at the time of the diagnosis nor in the future. It just means that you have a higher risk of it happening;
- There are several available options to help women manage this increased risk of breast cancer.